Hip, Leg and Foot Problems
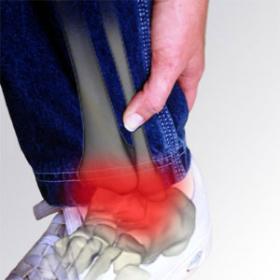 Hip, leg and foot problems are commonly the result of joint dysfunction and nerve interference in the spine, pelvis or lower limb.
Hip, leg and foot problems are commonly the result of joint dysfunction and nerve interference in the spine, pelvis or lower limb.
Hip, leg or foot pain can be debilitating, making it hard to do day-to-day activities and work effectively.
Chiropractors are trained to identify the cause, assist in its management, and give advice for prevention.
Why do problems occur?
Common causes are:
- Lumbar or sacro-iliac subluxation.
- Malfunction of joints in the pelvis and lower back may interfere with nerves exiting from the spine, resulting in referred pain, numbness, pins and needles or weakness in the limb.
- Nerves to the blood vessels may be affected and cause hot or cold changes, or pain in the Iimb.
- Malfunction or imbalance of other joints. This may arise at the hip, knee, ankle or foot.
- Muscle or tendon injury / imbalance.
- Referred pain Arising from abnormal function in other areas of the spine, organs of the abdomen or pelvis. Vascular disturbance may be a factor.
- Osteoarthritis. Injury and poor function of joints can cause premature wear and tear, leading to osteoarthritis. Correct joint alignment, mobility, and muscle balance are essential in preventing degenerative change.
- Lumbar and sacro-iliac subluxation, malfunction of other joints and muscle/ tendon injury most frequently arise from:Sudden trauma may include injuries from sporting and car accidents, or from falls, knocks and jolts.
- Over-use / excessive loading – resulting from repetitive stresses from work, poor posture, carrying school bags on one shoulder, sporting activities, poor bedding or sleep patterns, incorrect footwear, etc.
Regular chiropractic care, exercise and a nutritious diet are major factors contributing to good health of your body’s framework.
Chiropractic approach
Many common problems such as sciatica, bursitis, runners knee, recurrent ankle and knee strains/sprains, shin splints and metatarsalgia respond well to chiropractic management.
Chiropractors recognise that poorly functioning joints of the spine or lower limb interfere with nerve pathways. This often leads to weakness, poor co-ordination and breakdown.
The chiropractic approach is to restore function by ;
- correcting subluxations (i.e. poorly functioning joints causing nerve irritation)
- improving muscle balance and strength advising on remedial exercises
- preventive procedures.
Chiropractors believe that prevention is far better than cure.
Regular chiropractic care helps reduce the likelihood of problems by assisting optimal balance and function of the spine and nervous system.
Schedule of Care
When consulted, a chiropractor may examine the spine, hip, leg and foot. X-rays may be taken. The chiropractor may also examine other areas seemingly unrelated such as the upper back and neck. Your chiropractor is interested in your overall health and also recognises that your problem may be caused by instability in another area.
A course of treatment to re-establish normal function will be recommended if it is considered chiropractic care would be beneficial.
Exercises and advice on reducing the effects of physical stress may be given.
Recommendations for ongoing care may be given to assist in the maintenance of health and prevention of future problems. Health care requires constant attention for maximum benefit.
References.
1. Bourdillon J, (1982)’Spinal Manipulation’, Heinemann Medical Books, London and Applefon-Cenfury-Croffs, New York, 3rd Ed..pp 205-207.
2. Homewood A E, (1979)’The Neurodynamics of fhe Vertebral Subluxation’ 3rd. Ed.Chap. XII.,XV pp235-236.
3. Lowther,D A, (1985) ‘The Effects of Compression and Tension on the Behaviour of Connective Tissues’, Aspects ot Manipulative Therapy,2nd.Ed.Churchill Livingstone pp.16-22.
4. Woo SL, Mathews JV, Akeson WH et al: (1975) ‘Connective Tissue Response to Immobility’. Arthritis Rheum 18(3): 257-264″
5. Frankel VH, Burstein AH, Brooks DB, (1971): ‘Biomechanics ot Internal Derangement ot the Knee: Pathomechanics as determined by Analysis of the Instant Centres of Motion.’ J. Bone Joint Surg.. 53A: 945-962.
6. Kessler R M,Hertling D,(1983) ‘Management of Common Musculoskeletal Disorders, Physical Therapy Principles & Methods’. Harper & Row, Philadelphia, Chap.2.